In stock markets where every tick of the clock can spell the difference between profit and loss, the concept of arbitrage often echoes through the halls of stock exchanges and financial institutions. As it helps people in making money from the stock market even under volatile conditions.
But what exactly is arbitrage, and how does it work?
In
this blog, we’ll introduce you to the mysteries of
arbitrage, explore its types, risks, rewards, and its
fascinating presence in the
Indian stock markets.
What is Arbitrage?
If you could buy a product for a lower price in one store and sell it for a higher price in another, you will surely make a decent profit in this whole arrangement without any fuss. Right?
Arbitrage is essentially the same concept, but
applied to financial assets.
At its core,
arbitrage is a financial strategy that exploits price
discrepancies for the same asset in
different stock
exchanges or at different times.
How Does Arbitrage Work?
The heart of arbitrage lies in the pursuit of risk-free profit. It operates on the concept that identical assets should have identical prices in an efficient market.
However, markets aren’t always perfectly efficient, and that’s where arbitrageurs come into play. They identify situations where the same asset is trading at different prices and take advantage of these price differentials.
The Different Types of Arbitrage
Arbitrage comes in various forms, each with its unique nuances but the underlying idea remains the same. Some of its common types include:
| Type of arbitrage | Description |
| Spatial arbitrage | Exploiting price differences for the same asset in different geographic locations. |
| Temporal arbitrage | Capitalizing on price disparities that occur over time. |
| Statistical arbitrage | Leveraging quantitative models and statistical analysis to identify mispriced assets. |
| Exchange arbitrage | Buying an asset on one exchange and selling it on another exchange at a higher price. |
| Futures arbitrage | Futures arbitrage is a trading strategy that seeks to profit from price discrepancies between the cash and futures markets for the same underlying asset. |
| Merger arbitrage | Buying shares in a company that is being acquired by another company at a price below the acquisition price. |
| Dividend arbitrage | Buying shares in a company that is about to pay a dividend and then selling them after the dividend has been paid. |
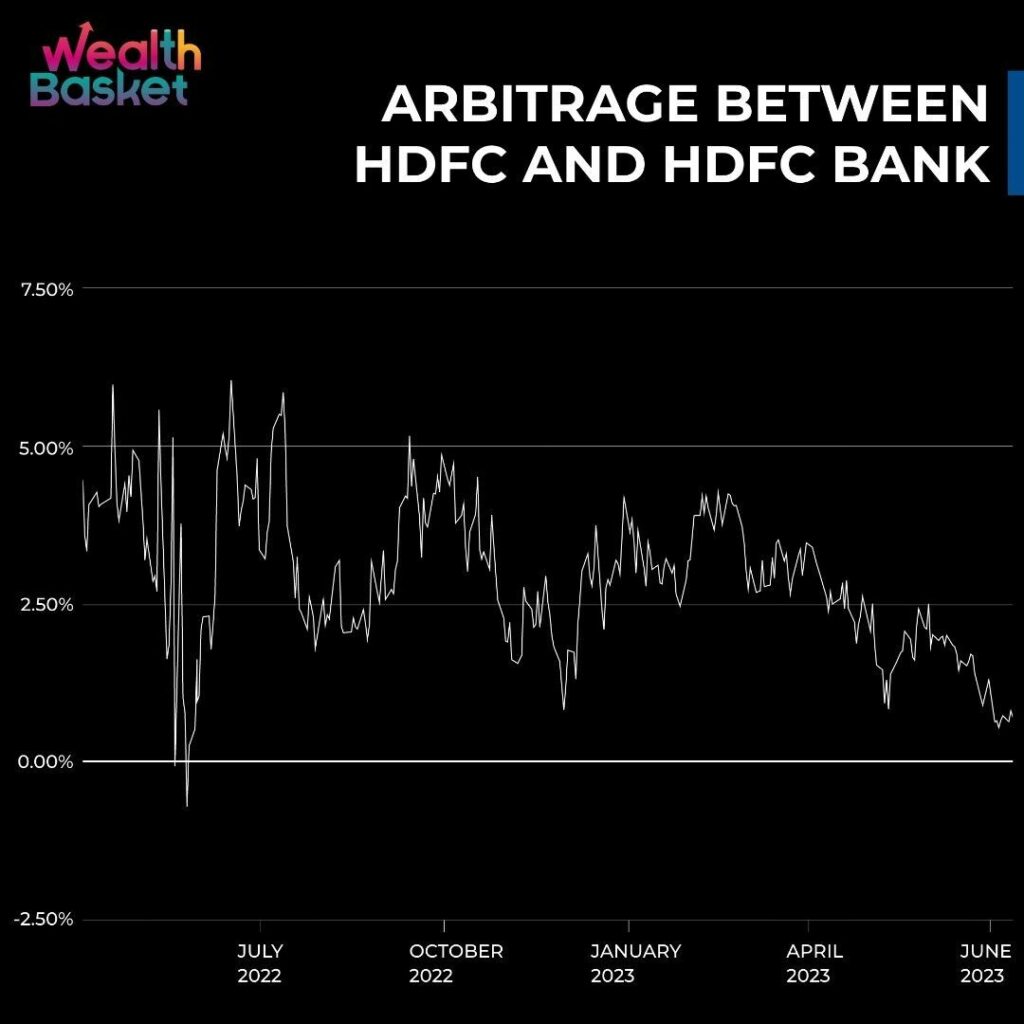
Example of Arbitrage from Indian Markets
In April 2022, HDFC Ltd. and HDFC bank decided to merge together into HDFC Bank to create India’s largest bank by assets. Accordingly for every 25 shares of HDFC Ltd, shareholders were supposed to get 42 shares of HDFC Bank.
This provided a good arbitrage opportunity for traders
and investors who bought shares of HDFC Ltd. which were
trading at a lower price compared to HDFC Bank and made
good money through this arbitrage opportunity.
You
can refer to the image below to see how the arbitrage
changed over time.
The Risks and Rewards of Arbitrage
Arbitrage is often viewed as a low-risk strategy because it aims to lock in profits regardless of market direction. However, it’s not without its challenges.
Risks can arise due to execution delays, market volatility, and unexpected events. The rewards, though, can be enticing, especially when arbitrage opportunities are efficiently seized.
Challenges of Arbitrage
Despite its potential, arbitrage in Indian markets isn’t a walk in the park.
Challenges such as:
- Liquidity constraints
- Regulatory complexities
- Technological hurdles
- High-frequency trading competition
can complicate arbitrage strategies.
To navigate the complexities and pitfalls of arbitrage successfully, investors need a combination of expertise, technology, and a keen understanding of market dynamics.
Diligent risk management and constant monitoring of arbitrage positions are also critical.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, arbitrage is a captivating aspect of the financial world, where opportunities exist for those who can decipher the intricacies. While it may not always guarantee vast fortunes, it certainly offers a compelling avenue for traders and investors seeking to use price differentials for generating profit.
FAQs
The rewards of arbitrage include potential profit with relatively low risk, while risks involve market volatility, transaction costs, and the possibility of prices not converging as expected.
In Indian stock markets, arbitrage opportunities can arise from price differences in stocks, commodities, or currency pairs traded on various exchanges.
An example is cash-futures arbitrage, where traders buy stocks in the cash market and simultaneously sell futures contracts on the same stocks to profit from price differences.
Challenges include high-frequency trading competition, regulatory constraints, and the need for advanced technology and data analysis.















